Mazda approaches safety with the same philosophy it applies to design and driving feel: support the driver, do not replace them. i-Activsense is Mazda’s suite of active safety and driver assistance technologies built to enhance awareness, reduce fatigue, and intervene only when a situation becomes critical. Rather than relying on aggressive automation, Mazda calibrates these systems to feel natural and predictable in real-world driving.
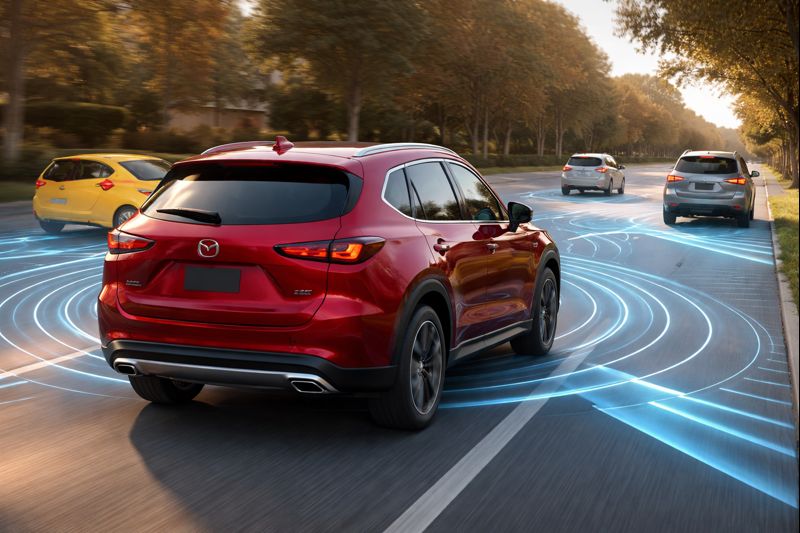

For drivers navigating Orange Park roads, suburban traffic patterns, and regional highways, i-Activsense is designed to work quietly in the background, providing information first and assistance second. Understanding how these systems function helps drivers use them correctly and confidently.
Active Safety Versus Passive Safety
Mazda separates safety into two complementary layers.
Passive safety focuses on protection during a collision. This includes body structure design, airbags, seatbelts, and energy management systems.
Active safety focuses on preventing collisions before they happen. i-Activsense belongs in this category. These technologies monitor surroundings, track vehicle behavior, and support driver decision-making in real time.
Mazda places strong emphasis on active safety because preventing an incident is always preferable to managing the aftermath.
How i-Activsense Works as a System
i-Activsense is not a single feature. It is a network of cameras, radar sensors, and vehicle control modules working together. Forward-facing cameras monitor lane markings, vehicles, and pedestrians. Radar sensors track distance and relative speed. The system continuously evaluates driver input, road conditions, and surrounding traffic.
What distinguishes Mazda’s approach is how the system responds. Alerts are designed to inform first. Assistance follows only if needed. Full intervention is reserved for moments when the risk becomes immediate and the driver does not respond.
This layered escalation helps preserve driver trust and engagement.
Mazda Smart Brake Support
Mazda Smart Brake Support is the foundation of i-Activsense. It monitors the road ahead to detect vehicles, pedestrians, and potential obstacles.
The system operates in stages:
- Visual and audible warnings alert the driver to a potential collision
- Brake assist increases braking force if the driver reacts but does not brake firmly enough
- Automatic braking engages only when the system determines a collision is likely and no driver response is detected
This design allows the driver to remain in control while providing a safety net in critical moments.
Blind Spot Monitoring and Rear Cross Traffic Alert
Blind Spot Monitoring uses rear-mounted radar sensors to detect vehicles approaching from adjacent lanes. When a vehicle enters the monitored zone, the system provides a visual alert in the side mirror.
Rear Cross Traffic Alert extends this awareness when reversing out of parking spaces. It scans left and right for approaching vehicles and issues warnings to help prevent low-speed collisions in crowded areas such as shopping centers and school parking lots.
These systems focus on awareness rather than intervention, supporting driver judgment where visibility is naturally limited.
Lane Departure Warning and Lane Keep Assist
Mazda clearly differentiates between warning and assistance.
Lane Departure Warning alerts the driver when the vehicle begins to drift out of its lane without a turn signal. Lane Keep Assist adds gentle steering input to guide the vehicle back toward the center of the lane.
Mazda intentionally avoids aggressive steering corrections. The assistance is subtle, designed to support attentive driving rather than override it. Drivers remain actively engaged with the steering wheel at all times.
Mazda Radar Cruise Control
Mazda Radar Cruise Control uses radar and camera data to maintain a set speed while adjusting following distance based on traffic conditions. When traffic slows, the system reduces speed smoothly. When conditions clear, it resumes the preset speed.
Mazda calibrates adaptive cruise control to prioritize smoothness and predictability. Acceleration and braking inputs are gradual, which reduces fatigue during long drives while keeping the driver mentally involved.
Driver Awareness and Responsibility
A defining characteristic of i-Activsense is Mazda’s emphasis on driver responsibility. These systems are designed to assist attentive drivers, not enable hands-off driving.
Mazda avoids framing i-Activsense as autonomous technology. Instead, it is positioned as a tool that enhances situational awareness and provides support when attention momentarily lapses.
This philosophy reinforces safe driving habits rather than encouraging reliance on automation.
Understanding System Limitations
i-Activsense systems rely on clear lane markings, visible road conditions, and properly functioning sensors. Weather, road debris, glare, and unusual traffic situations can affect performance.
Drivers must remain aware of their surroundings and be prepared to take control at all times. Understanding these limitations is essential for using driver assistance features safely and effectively.
Why Mazda’s Safety Approach Feels Different
Many driver assistance systems on the market prioritize assertive intervention. Mazda takes a different approach by prioritizing predictability and subtlety. Alerts arrive when they matter. Assistance feels supportive rather than corrective. Intervention occurs only when necessary.
This calibration builds confidence over time. Drivers learn what to expect from the system and trust it without feeling overridden.
Safety Designed for Real Roads
For drivers in and around Orange Park, daily driving includes suburban traffic, school zones, highway merges, and unpredictable conditions. i-Activsense is designed to support these environments by enhancing awareness rather than demanding attention.
Mazda’s approach to safety reflects a belief that the safest driver is an informed and engaged one. By supporting the driver instead of replacing them, i-Activsense delivers a safety experience that feels natural, respectful, and aligned with how people actually drive.